Airflow Scheduling Engine Example
In the following sections, we will walk through a complete example to demonstrate how to integrate the third-party scheduling engine Airflow into Apache InLong to create an offline data synchronization from Pulsar to MySQL.
Deployment
Install InLong
Before we begin, we need to install InLong. Here we provide two ways:
- Docker Deployment (Recommended)
- Bare Metal Deployment
Add Connectors
Download the connectors corresponding to Flink version, and after decompression, place sort-connector-jdbc-[version]-SNAPSHOT.jar in /inlong-sort/connectors/ directory.
Currently, Apache InLong's offline data synchronization capability only supports Flink-1.18, so please download the 1.18 version of connectors.
Create Clusters And Data Target
When all containers are successfully started, you can access the InLong dashboard address http://localhost, and use the following default account to log in.
User: admin
Password: inlong
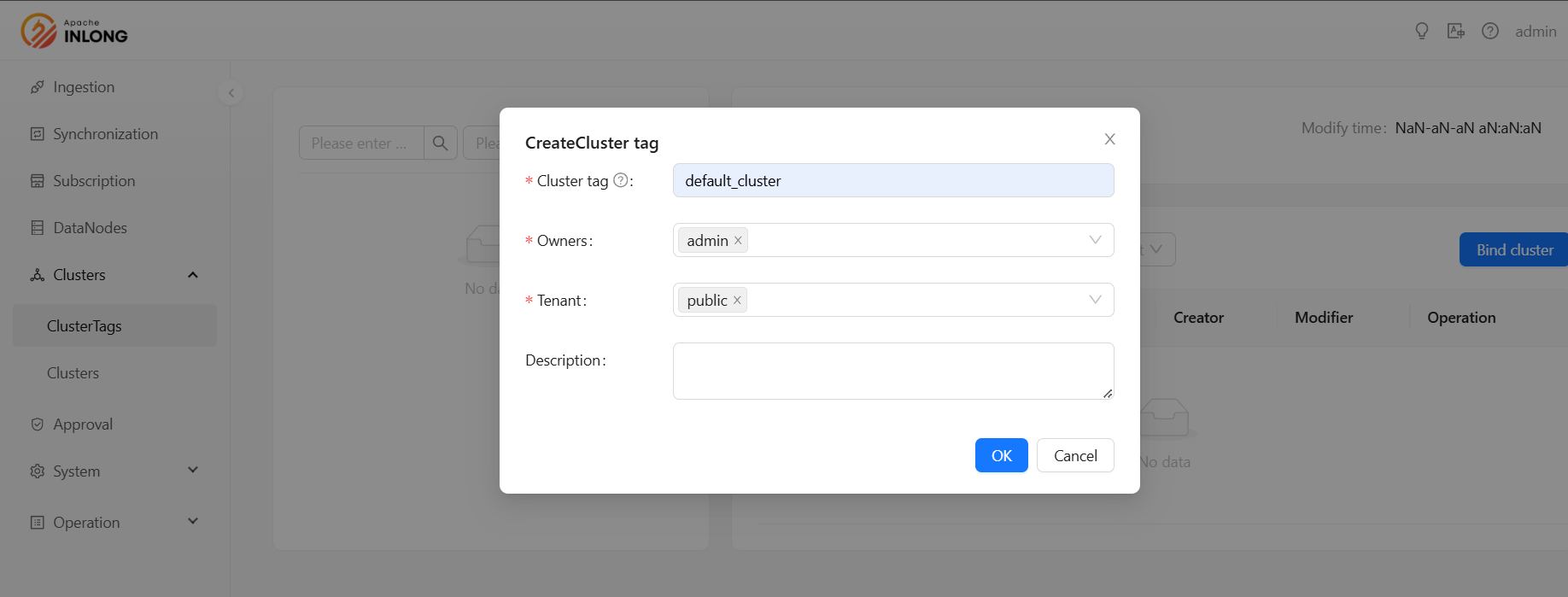
Create Cluster Tag
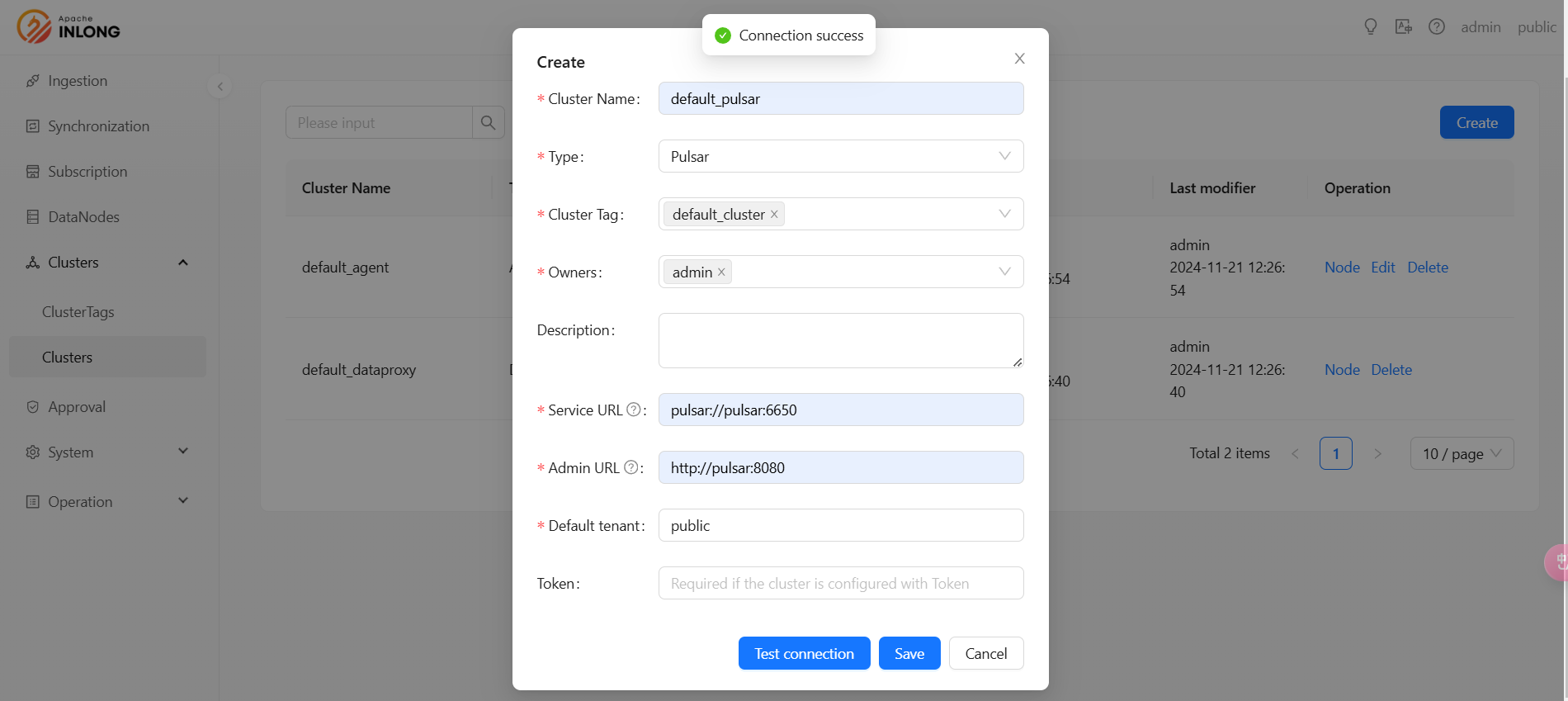
Register Pulsar Cluster
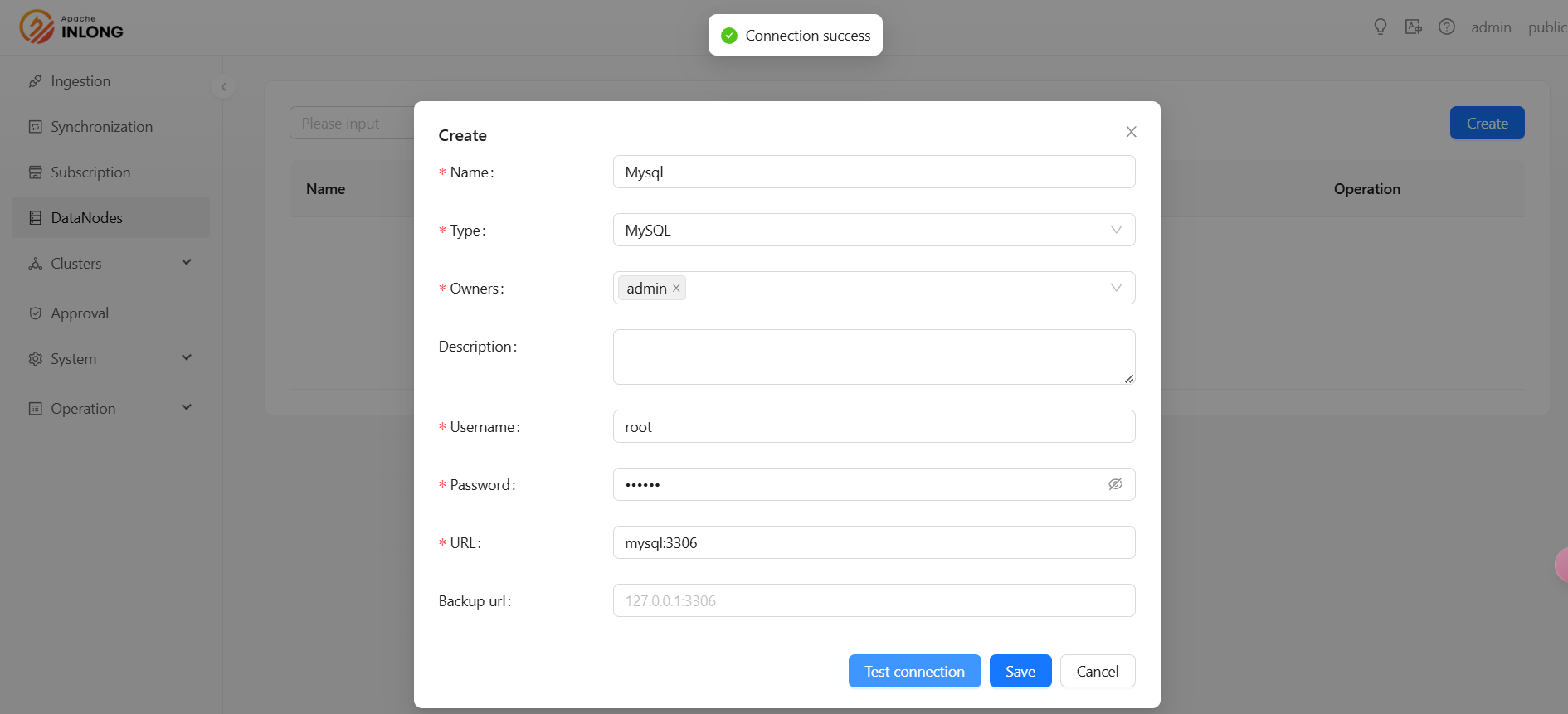
Create Data Target
Execute the following SQL statement:
CREATE TABLE sink_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
create_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
Airflow Initialize
Get Original DAG
They can be obtained from InLong.
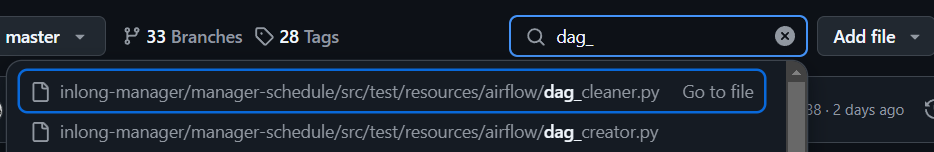
Airflow does not provide an API for DAG creation, so two original DAGs are required.
dag_creatoris used to create offline tasks, anddag_cleaneris used to clean up offline tasks regularly.
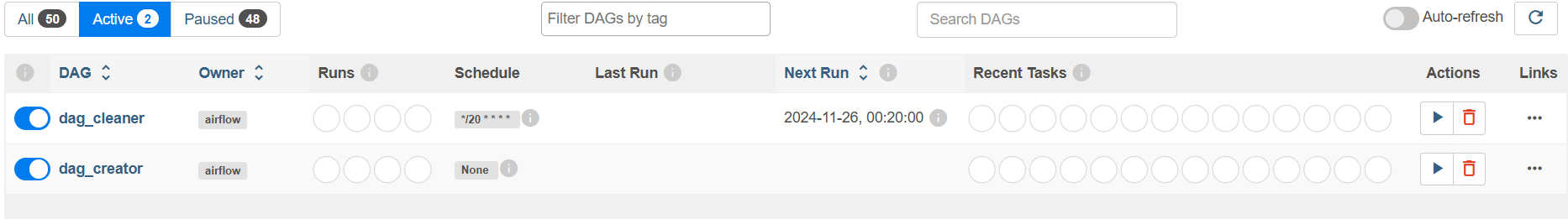
Create Original DAG
Place the DAG file in the Airflow default DAG directory and wait for a while. The Airflow scheduler will scan the directory and load the DAG:
Airflow REST API
By default, Airflow will reject all REST API requests. Please refer to the Airflow official documentation for configuration.
Configure InLong Manager
Modify the configuration file according to the configuration file requirements and restart InLong Manager.
# InLong Manager URL accessible by the scheduler
schedule.engine.inlong.manager.url=http://inlongManagerIp:inlongManagerPort
# Management URL for Airflow
schedule.engine.airflow.baseUrl=http://airflowIP:airflowPort
# Username and password for Airflow REST API authentication
schedule.engine.airflow.username=airflow
schedule.engine.airflow.password=airflow
# Connection used to save InLong Manager authentication information
schedule.engine.airflow.connection.id=inlong_connection
# The ids of the two original DAGs
schedule.engine.airflow.cleaner.id=dag_cleaner
schedule.engine.airflow.creator.id=dag_creator
Task Creation
Create Synchronization Task
Create Data Stream Group
Please refer to the following steps: Quartz Scheduling Engine Example
Create Airflow Offline Task
After approval and configuration, InLong Manager will trigger dag_creator through the Airflow API to create the offline task DAG:
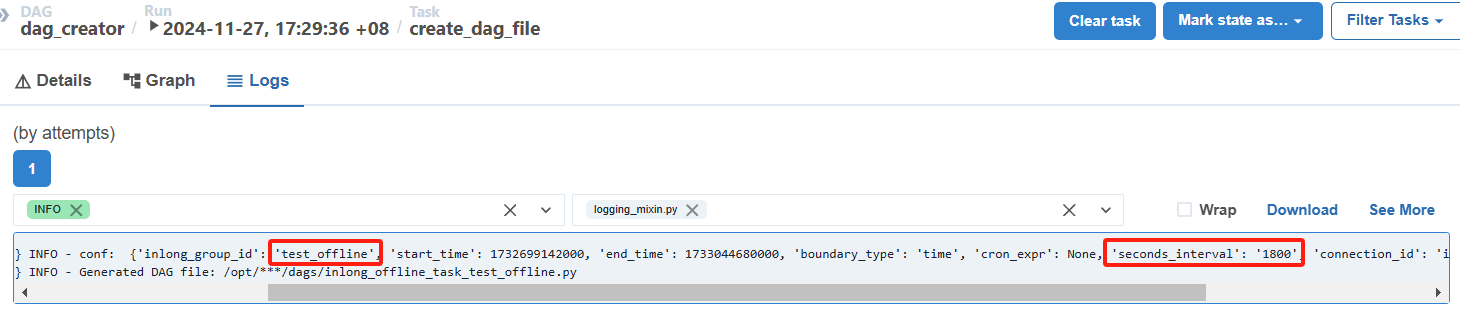
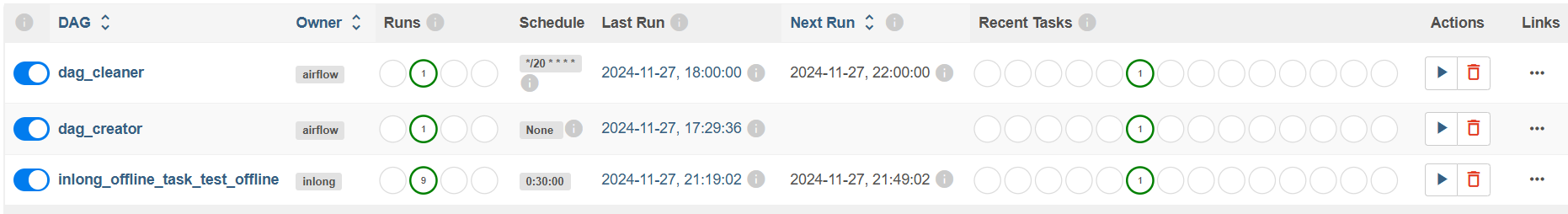
Offline task DAG may not be scheduled immediately, because Airflow will scan DAG files regularly and add them to the schedule, so it may take some time.
The offline task execution results are as follows:
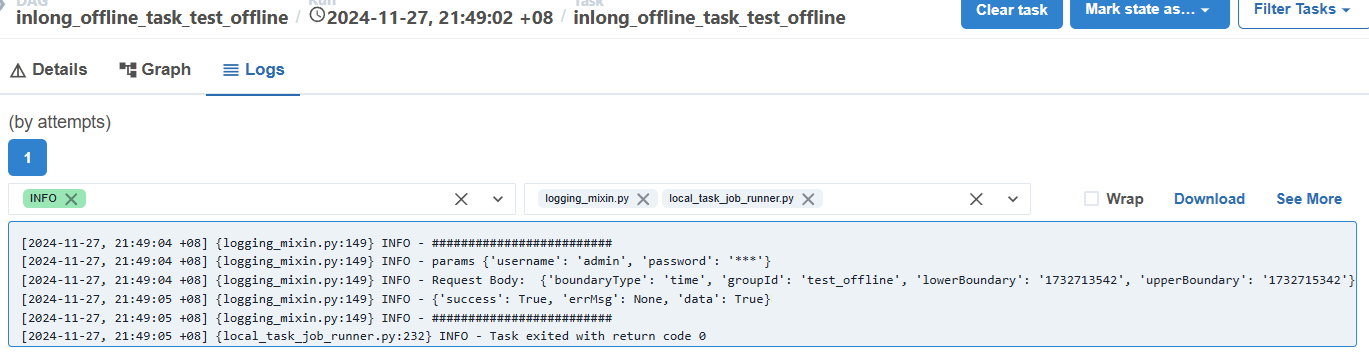
Airflow will periodically call the interface provided by InLong Manager to submit Flink tasks according to the configuration in the
Create Data Stream Groupsection. This is why the authentication information of InLong Manager needs to be saved in theConfigure InLong Managersection.
Test Data
Sending Data
Use the Pulsar SDK to produce data into the Pulsar topic. An example is as follows:
// Create pulsar client and producer
PulsarClient pulsarClient = PulsarClient.builder().serviceUrl("pulsar://localhost:6650").build();
Producer<byte[]> producer = pulsarClient.newProducer().topic("public/default/test").create();
// Send a message
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
// The field separator is |
String msgStr = i + "|msg-" + i;
MessageId msgId = producer.send(msgStr.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
System.out.println("Send msg : " + msgStr + " with msgId: " + msgId);
}
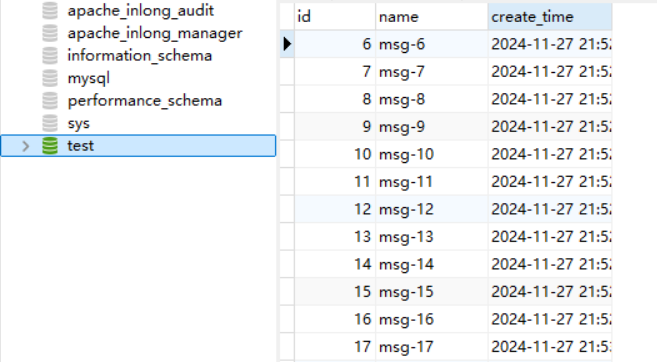
Data Validation
Then enter MySQL to check the data in the table: